
Introduction
Africa’s rapid growth in Internet communications is creating a wide range of opportunities but also a wide range of vulnerabilities. This rapid shift to online activities has created a goldmine for cyber criminals. Since legal systems and people trained to fight cyber crimes are scarce, many economies are at risk. There is, however, a growing awareness of threats, with governments and businesses taking steps to implement cybersecurity policies and develop a qualified workforce to combat these challenges.
Quad9 is a global DNS service that offers enhanced cybersecurity measures, privacy protection, and improved Internet performance. Quad9's ability to block access to malicious websites is of paramount importance to the nascent African Internet economies. Quad9 helps keep people and businesses safe online. For example, it blocks such threats as phishing scams, malware, and ransomware. It is especially important for organizations that handle sensitive information, like governments, schools, and hospitals. The implementation of Quad9 in Africa is a low-cost, high-impact solution to enhance digital security, performance, and privacy. Quad9 is present in more than 40 locations in 30 African countries:

To safeguard our clients, Quad9 uses continuously updated threat information to block DNS lookups of malicious host names. This proactive measure protects computers, mobile devices, and other Internet systems from a broad spectrum of cyber threats, such as malware, phishing, spyware, and botnets. Every time an Internet-connected device that uses the Quad9 service tries to access a site hosting malware, Quad9 works silently in the background to prevent the connection from being made, and, in effect, saves its user from being infected by malware.
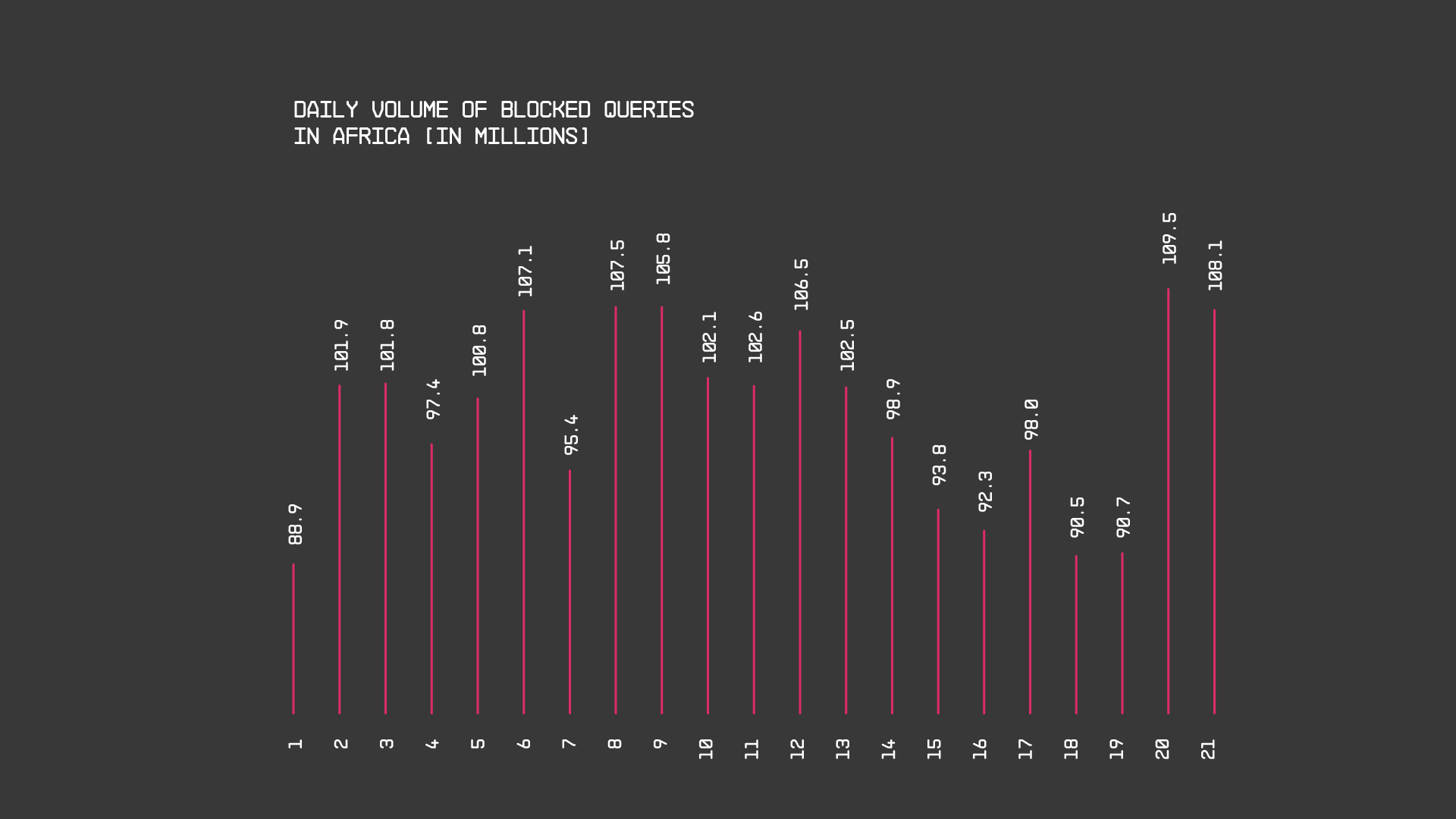
This report provides an overview of the security threats that Quad9 DNS blocked for current users in Africa between March 1 and March 21, 2024. In total, across Africa, Quad9 blocked more than 2.1 billion malicious queries, for an average of 100 million blocked queries daily:
Most Prevalent Threats
Thanks to Quad9 services, African users have been shielded from a variety of cyber threats, including phishing, stalkerware, spyware, and malvertising. In this section, we discuss the main threats to African Internet users.
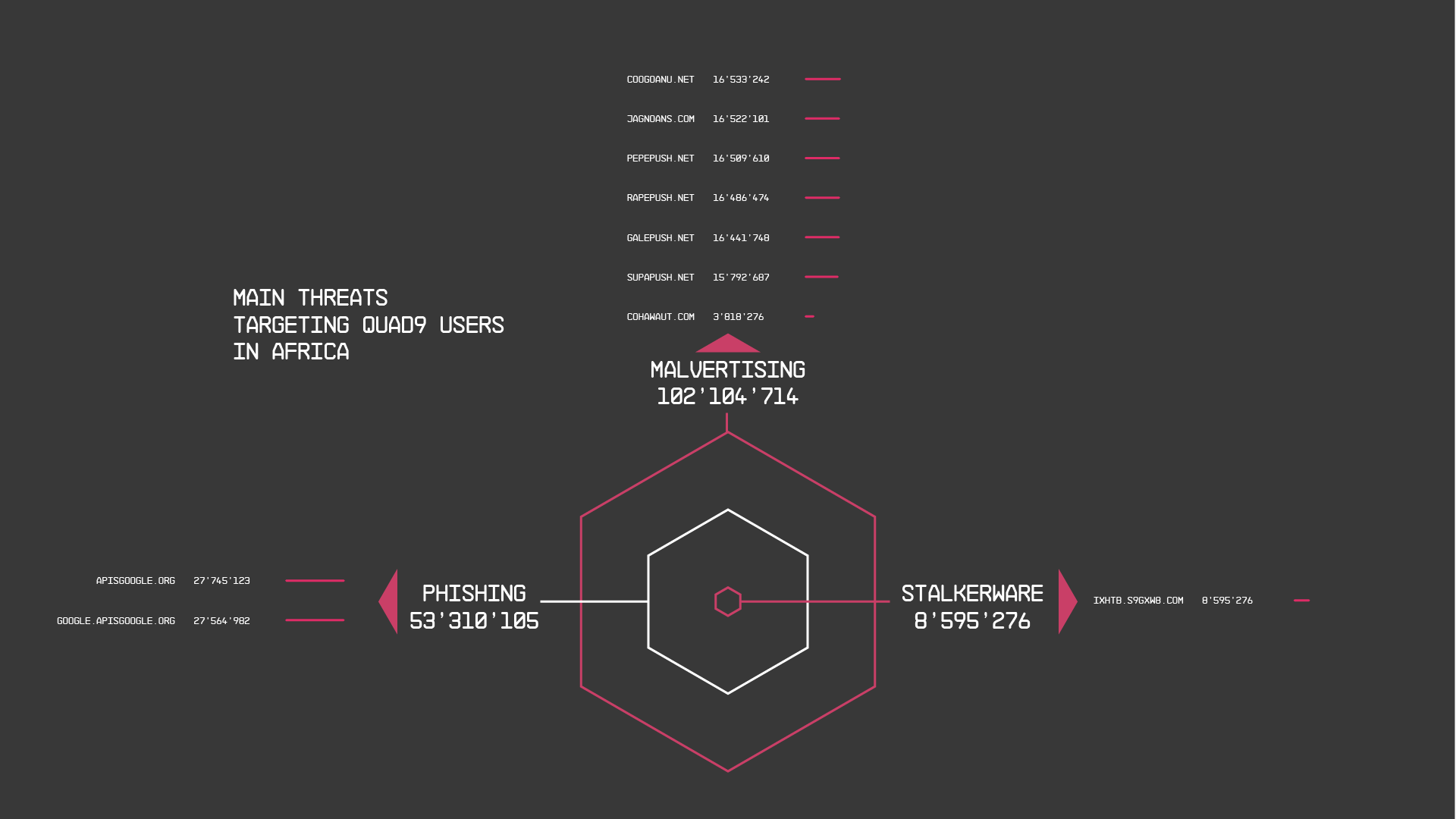
Quad9 security systems successfully protected African users from phishing attacks that cleverly mimicked Google (apisgoogle and google.apisgoogle). Phishing attempts like those are a deceptive tactic in which cyber criminals create emails, text messages, or fake websites designed to look legitimate. Their goal is to trick a user into revealing sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, or social security numbers. Once stolen, such information can be used to perform other cyber attacks or to steal the victim's identity.
But phishing was not the only threat our defenses have encountered. Malvertising campaigns, likely orchestrated by the Omnatour network, were also busy compromising vulnerable websites. In this kind of attack, users visit legitimate websites that have been infected with a malicious code, which subsequently works behind the scenes, targeting victims with unwanted and potentially dangerous advertisements that appear as pop-ups or intrusive push notifications. Clicking on these ads might lead to further malware infections or frauds.
Particularly concerning is the rise of stalkerware targeting African users. Disguised as everyday apps like calculators or calendars, such malicious applications silently steal users’ critical and private personal data, which becomes a stalker's weapon, potentially used for harassment, blackmail, or impersonation. The danger lies in stalkerware's ability to disguise itself, hidden within seemingly harmless apps.
Conclusions
Over the years, it has become easier and cheaper for hackers to attack Internet users. As Africa embraces the digital age, it faces a critical need to strengthen cybersecurity measures to protect its growing online space. Quad9 is at the forefront of this effort, aiming to enhance the Internet's security and stability, thereby diminishing users' susceptibility to cyber threats, and augmenting the efficiency of their online interactions – even in the face of escalating cyber attacks.
By preventing connections to malicious sites, Quad9 eliminates exposure to risks before they are downloaded to computers or their victim can see the fraudulent website. The inability to reach a malicious host means that defenses, such as virus protection, or user-based detection, such as certificate examination, are never called into action1.
Quad9 is a non-profit organization based in Switzerland whose main goal is to protect end users against harm while providing them private and trustworthy access to DNS resources, all at no cost to the end user.
Quad9 is a non-profit organization based in Switzerland whose main goal is to protect end users against harm while providing them private and trustworthy access to DNS resources, all at no cost to the end user.
1 Quad9’s DNS-based blocking cannot prevent all risks but only those that are attributable to attacks that have involve a DNS component, which is estimated to be 30% of all cyber attacks. https://www.globalcyberalliance.org/wp-content/uploads/GCA-DNS-Security-Report.pdf
Observations on African Cybersecurity Landscape
Authored by: Emilia Cebrat-Maslowski



